Threats:
(1) Throughout Europe poaching is one of the major threats to lynx survival.
(2) Lynx are hunted in Norway and Estonia, and subject to some lethal control in other countries like Sweden, Finland, Romania and Latvia. There is a need to ensure that quotas here remain at a sustainable level, although currently many of these countries are only issuing very small quotas.
(3) The Balkan population is very small, completely isolated, and lives in habitats with a poor prey base. This population is the one of greatest concern in Europe today.
(4) Lynx in some parts of their range (e.g. NE Poland, Belarus and Lithuania) have a very fragmented distribution, living in forest patches isolated from each other by farmland.
(5) Many of the reintroduced populations in central Europe are very small and potentially inbred such that there is a need for introducing more animals from the Carpathians and promoting greater connectivity.
Distribution:
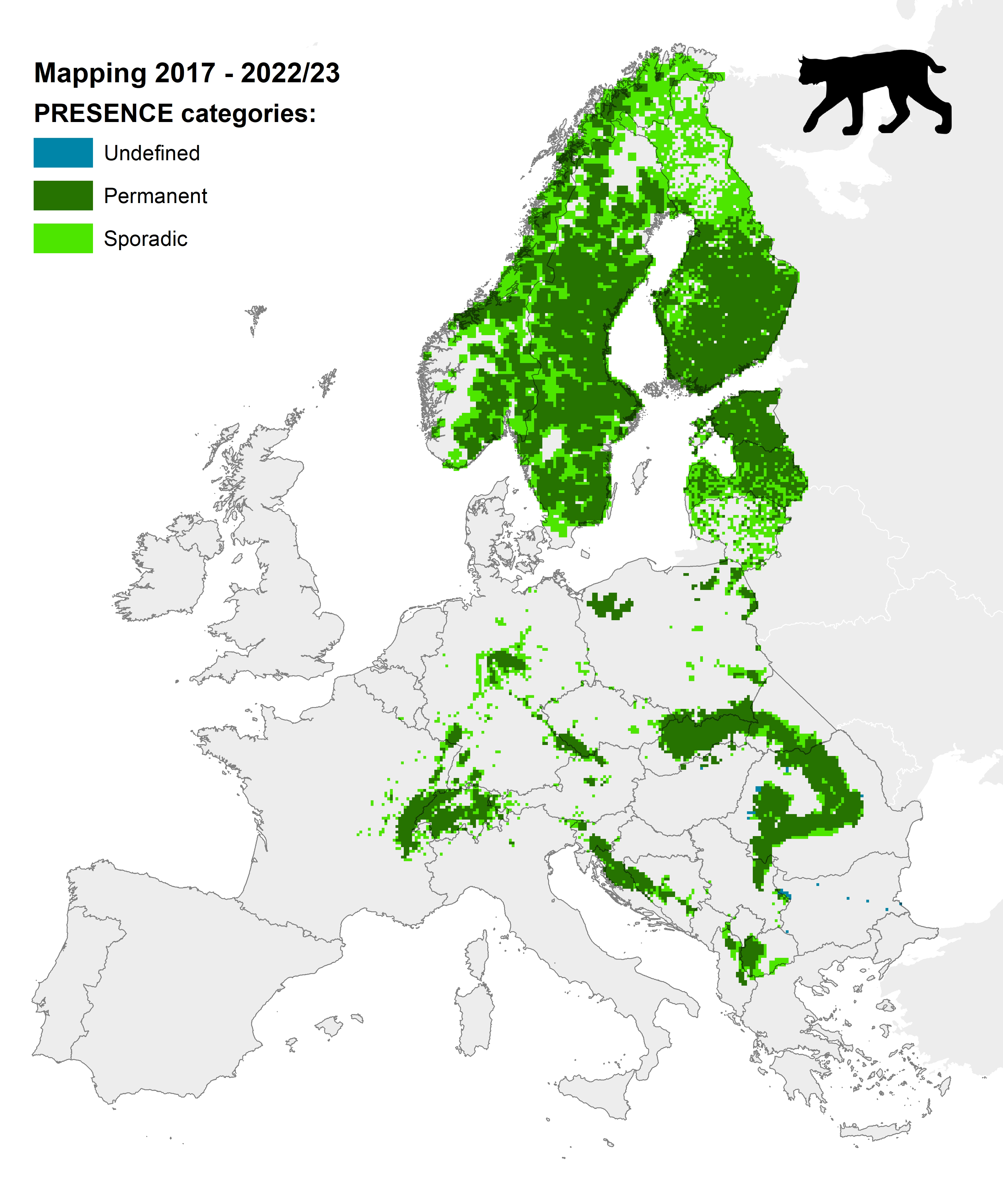
Distribution maps 2012-2016 available from Data Dryad and for 2017-2022/23 available from Data Dryad.
Status:
9,400 in Europe (Source: LCIE Status Assessment 2017-2022/23)
11 populations and 2 occurrences
|
Population name
|
Countries
|
Size
(2017-2022/23)
|
Trend
|
|
Scandinavian
|
Norway, Sweden
|
1820
|
Increasing
|
|
Karelian
|
Finland
|
2483
|
Stable
|
|
Baltic
|
Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Ukraine
|
1555
|
Increasing
|
|
Bohemian-Bavarian-Austrian
|
Czech Republic, Germany, Austria
|
135
|
Increasing
|
|
Carpathian
|
Romania, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Czech Republic, Hungary, Serbia, Bulgaria
|
2687
|
Increasing
|
|
Alpine
|
Switzerland, Slovenia, Italy, Austria, France
|
255
|
Increasing
|
|
Jura
|
France, Switzerland
|
more than 69
|
Slowly increasing
|
|
Vosges Palatinian
|
France, Germany
|
more than 12
|
Increasing
|
|
Dinaric
|
Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina
|
130
|
Stable or decrease
|
| Harz Mountains |
Germany |
46 |
Slowly increasing |
|
Balkan
|
North Macedonia, Albania, Kosovo*, Montenegro, Serbia |
34
|
Stable
|
| Pommerian Occurrence |
Poland |
31 |
Increasing |
| Black Forest / Swabian-Jura Occurrence |
Germany |
5 |
Unknown |